Presidential Election of 1952
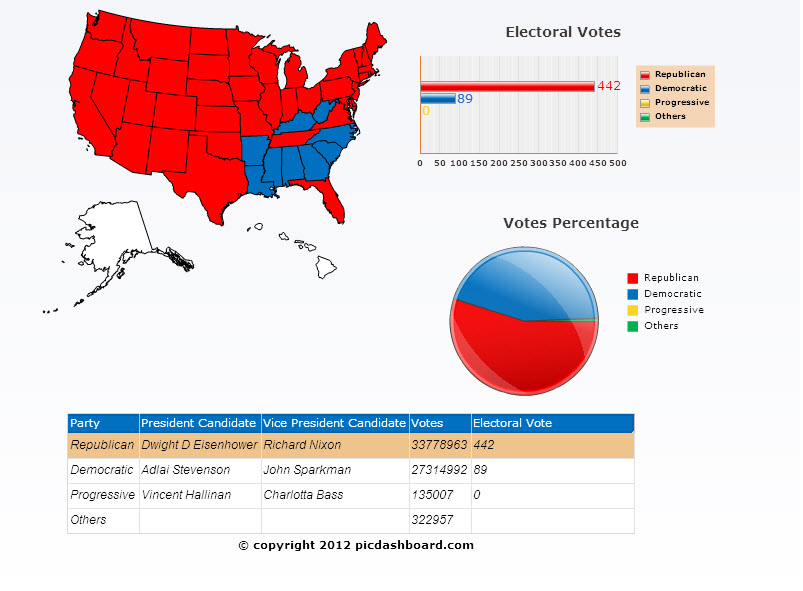
In the United States of America presidential elections of 1952, Republican presidential candidate Dwight D. Eisenhower swept the election results with a victory margin of more than 10%.
Eisenhower won the election helped by his huge popularity for his role as the supreme commander of the Allied forces in the World War II.
1952 Presidential Election Results
| Republican Party | |
| Adlai Stevenson | Democratic Party |
|
Political Situation:
1. Second Election after the end of the disastrous World War II.
2. Due to the decisive role of Russia in the defeat of Hitler's forces, Communism spreads across the world.
3. Intensification of Cold war.
4. North Korea attacks South Korea.
Close States (margin<6%):
Delaware, Kentucky, Louisiana, Missouri, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Tennessee, West Virginia
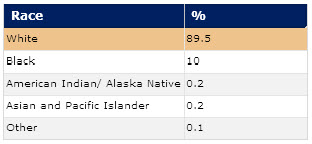
Population by Race for the United States : Year 1950
|
|
Republican Party Agenda:
1. Guard Education.
2. Remove Corruption.
3. Communistic subversive or pinkish influence need to be uprooted
from responsible places of the government
4. Reduce budget deficit.
5. Women in key positions.
Biography of Dwight D. Eisenhower ( Republican presidential candidate ):
1. Supreme Commander of the Allied forces in Europe.
2. Oversaw the routing of the Hitler's forces on the Western front in Europe. Enabled the emergence of US as one of the
two Super Powers after the World War II.
3. Oversaw the invasion of Sicily, Italy.
4. Eisenhower was born on Oct 14 1890 in Denison, Texas.
Democratic Party Agenda:
1. Resistance to Soviet pressure.
2. Not to precipitate war through hastiness.
3. Continue to protect the producers of basic agricultural commodities under the terms of a
mandatory price support program at not less than 90 per cent of parity.
Biography of Adlai Stevenson ( Democratic presidential candidate ):
1. One of most successful Governors in the history of IllinOis, with
brilliant record of reform, economy and efficiency.
2. Postwar diplomatic experience as Special Assistant to Secretary of
State at United Nations Charter Conference; U.S. Minister in London and Chief Delegate to U.N. Preparatory
Commission; U.S. Delegate to first sessions of United Nations in London and New York.
3. Wartime service as Assistant to the Secretary of the Navy, member of Air Force Mission to Europe, Chief of Economic
Mission to Italy.
4. Depression era service in Department of Agriculture, one of the architects of the farm program that saved American
farm families.
